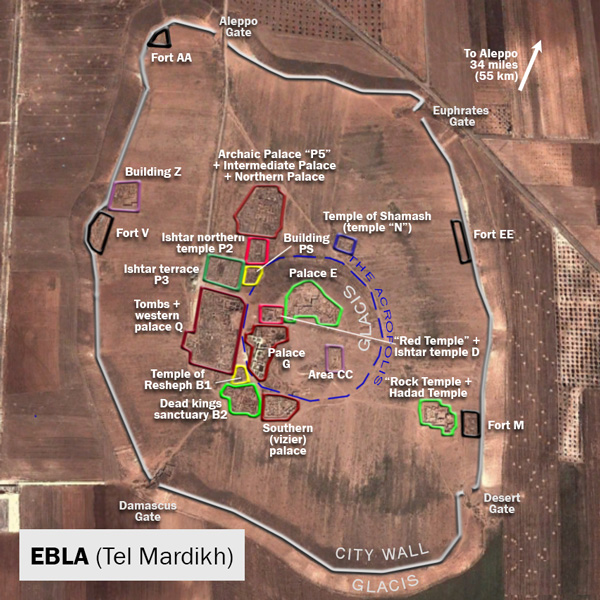
Significance of Ebla
Ebla was an ancient city that flourished from about 3500-1600 BCE. At its peak, it was the capital of a kingdom that stretched from what is now Lebanon to the Euphrates River.
During this period, the famous Ebla tablets were written. These tablets, about 2500 in all, constitute one of the oldest libraries ever found in the Middle East. They are written in cuneiform in both the Sumerian and Eblaite languages. These texts provide us with insights into the politics, economy, and culture of northern Mesopotamia of the third millennium BCE.
Want to dive deeper?
- “Ebla: Official Site of the Italian Archaeological Mission in Syria” (in English, many pages, including bibliography about excavations)
- “Eblaite: Online Resources” (includes extensive bibliography)
- Jeff A. Benner, “The Archives of Ebla and the Bible“
- Paolo Matthiae – Ebla: An Empire Rediscovered (New York: Doubleday, 1981).
- Giovanni Pettinato – The Archives of Ebla: An Empire Inscribed in Clay (New York: Doubleday, 1981).
- Giovanni Pettinato – Ebla: A New Look at History (Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University, 1991).
- “Ebla” (Wikipedia article)
